Cold storage warehouses play a vital role in Australia’s supply chain, particularly in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Maintaining precise temperature control while ensuring inventory accuracy and operational efficiency is critical. A WMS in Cold Storage Warehouses Australia offers advanced tools to address these unique challenges and drive productivity. By automating temperature-sensitive stock management, businesses can prevent spoilage and comply with strict regulatory requirements. Additionally, real-time monitoring and reporting enhance visibility, allowing warehouse managers to respond swiftly to any fluctuations or disruptions.

Challenges in Cold Storage Warehousing
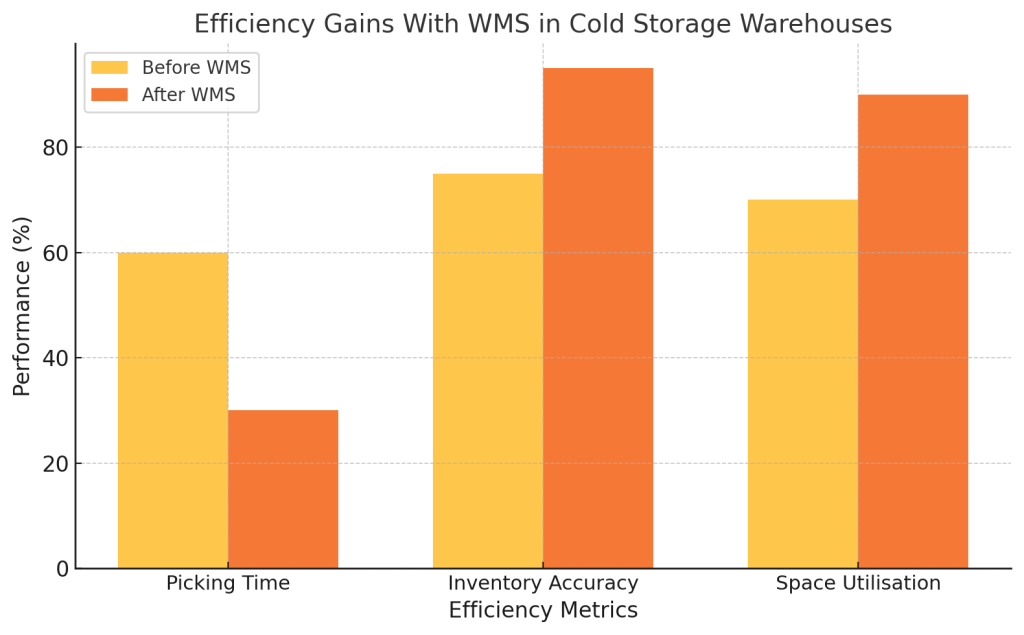
Cold storage warehouses face distinct operational challenges that require specialised solutions. Key issues include maintaining consistent temperature levels, ensuring regulatory compliance, and optimising space for perishable goods. WMS in Cold Storage Warehouses Australia helps streamline operations by automating temperature monitoring and inventory tracking. Additionally, advanced analytics provide insights that improve energy efficiency and reduce waste, ensuring businesses can maintain quality standards while enhancing overall productivity.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Strict temperature control is essential to prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.
- Inventory Accuracy: Managing perishable goods requires real-time updates to minimise waste.
- Space Optimisation: Limited storage capacity necessitates efficient space utilisation.
- Compliance Requirements: Meeting Australian regulatory standards for cold storage is non-negotiable.
The Role of WMS in Addressing Cold Storage Challenges
A WMS for cold storage provides tools to optimise workflows, ensure compliance, and reduce costs while maintaining strict temperature controls. By automating inventory tracking and order processing, businesses can minimise spoilage and enhance overall efficiency.
- Temperature-Sensitive Inventory Tracking
A WMS monitors and records temperature data for individual storage zones, ensuring that products remain within specified conditions.
Benefit: Prevents spoilage and ensures compliance with Australian food safety regulations. - Real-Time Inventory Management
Tracks product locations, batch numbers, and expiration dates in real-time to minimise waste.
Benefit: Reduces inventory loss by optimising stock rotation (FIFO/LIFO strategies). - Space Optimisation
Cold storage is expensive, making efficient use of space critical. A WMS optimises pallet storage based on size, weight, and temperature requirements.
Benefit: Maximises capacity while ensuring easy access to products.
Challenges and WMS Solutions for Cold Storage Warehouses
| Challenge | Impact on Operations | WMS Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensitivity | Spoilage or product recalls due to improper storage. | Monitors and records real-time temperature data. |
| Inventory Inaccuracy | Wastage and stockouts due to poor inventory visibility. | Real-time tracking and automated stock updates. |
| Limited Space | High operational costs due to inefficient storage. | Space optimisation tools for efficient utilisation. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Penalties or shutdowns for failing to meet standards. | Automated compliance tracking and reporting. |
| High Labour Costs | Longer picking times in cold environments. | Route optimisation and automated workflows. |
Leveraging Automation and Labour Optimisation in Cold Storage Warehouses
Cold storage environments pose unique challenges for warehouse workers, such as low temperatures and limited mobility due to protective gear. WMS in Cold Storage Warehouses Australia integrated with automation and labour optimisation tools helps overcome these hurdles, improving efficiency and reducing costs. By streamlining workflows and enhancing real-time inventory tracking, businesses can maintain productivity while ensuring compliance with strict storage requirements.
Automation in Cold Storage Warehouses
Automation minimises manual intervention in cold storage environments, allowing for faster operations and enhanced safety. Integrating a WMS with automated tools like conveyor systems, robotic pallet movers, and barcode scanners eliminates inefficiencies.
Key Automation Features for Cold Storage:
- Automated Picking and Packing: Reduces time spent in cold zones, minimising worker exposure.
- Temperature Monitoring Sensors: Sync with WMS to ensure real-time tracking of storage conditions.
- Batch and Lot Management: Tracks products by expiration dates to implement FIFO or LIFO strategies effectively.
Benefits of Automation:
- Speeds up processes while maintaining accuracy.
- Reduces energy consumption by optimising workflows.
- Improves worker safety by limiting exposure to low temperatures.
Labour Optimisation with WMS
Efficient workforce management is critical in cold storage, where employee productivity can be affected by environmental conditions. A WMS helps streamline labour allocation by prioritising tasks and reducing unnecessary movement.
Labour Optimisation Features:
- Task Assignment: Assigns tasks based on proximity and priority, reducing travel time.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks worker productivity to identify bottlenecks and training needs.
- Dynamic Scheduling: Adjusts staffing levels based on demand fluctuations.
Benefits of Labour Optimisation:
- Enhances productivity even in harsh working conditions.
- Reduces fatigue and increases worker satisfaction.
- Minimises operational delays during peak demand periods.
Advanced Strategies and the Future of Cold Storage WMS
The evolving demands of cold storage warehouses in Australia require not only efficient operations but also forward-thinking strategies to remain competitive. Leveraging advanced WMS features and adapting to industry trends can further enhance productivity and compliance.
Advanced Strategies for Cold Storage Warehouses
- Integration With IoT Devices
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors integrated with a WMS provide real-time temperature monitoring and inventory tracking.
Benefit: Improves response times to temperature fluctuations, preventing spoilage and ensuring compliance. - Blockchain for Traceability
Blockchain technology enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable records of product storage conditions and movements.
Benefit: Builds trust with consumers and regulatory bodies by proving product authenticity and safety. - Energy-Efficient Practices
Energy consumption is a significant cost in cold storage. A WMS can optimise workflows to minimise the use of refrigeration systems during peak energy pricing periods.
Benefit: Reduces operational costs and supports sustainability initiatives. - Cross-Docking
Implementing cross-docking reduces storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound shipments.
Benefit: Minimises the need for prolonged storage in cold conditions.
Future Trends in Cold Storage WMS
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Forecasting | Predicts demand and optimises inventory levels. | Reduces waste and ensures stock availability. |
| Robotic Automation | Uses robots for picking and pallet movement. | Enhances speed and reduces labour dependency. |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Focuses on energy-efficient workflows and reduced waste. | Lowers costs and aligns with environmental goals. |
| Mobile WMS Solutions | Allows workers to access WMS data via mobile devices. | Improves productivity and flexibility. |
| Cloud-Based WMS | Provides scalability and remote access for cold storage facilities. | Enhances collaboration and operational agility. |
Conclusion: Empowering Cold Storage Warehouses With WMS
For Australian cold storage warehouses, a WMS is not just a tool—it’s a strategic asset. It ensures compliance with stringent regulations, reduces waste, and improves operational efficiency, all while managing the unique challenges of temperature-sensitive inventory. Additionally, real-time data tracking enables proactive decision-making, helping businesses prevent stock losses and optimize resource allocation.
As the industry moves toward greater automation, IoT integration, and sustainable practices, adopting an advanced WMS positions warehouses for long-term success. Whether handling pharmaceuticals, frozen foods, or agricultural products, a WMS tailored for cold storage can transform operations, enabling businesses to thrive in a competitive market. Learn more about optimizing your warehouse with warehouse management software designed to meet the specific needs of Australian businesses.

